Follow this guide to set up hosted authentication for your Android apps.
Requirements
Section titled “Requirements”- Android Studio Bumblebee
- Kotlin Plugin 1.5.30
- Android minimum SDK 21, target SDK 32
Before You Begin
Section titled “Before You Begin”- If you haven’t already, register app on provider’s console. Please, use Create a Google Application guide as a reference.
- Obtain
provider_client_idandprovider_client_secretfrom provider. - Specify the Nylas callback URL
https://api.us.nylas.com/connect/callbackandhttps://api-staging.us.nylas.com/connect/callbackto your authorized or trusted redirect URI’s.
Step 1: Create an Integration
Section titled “Step 1: Create an Integration”Integrations are the provider you want to connect to the Nylas platform. Integrations let you add additional functionality to your Nylas accounts be connecting to services such as Google.
You only need to create an Integration once per provider and environment. If you have already created an Integration skip to Step 2.
Create a new Bearer API key for your Nylas application you’ll use for your API authentication.
- Get (or create new) API key for your Nylas Application
- Include in the header of your request like
Authorization: Bearer <NYLAS_API_KEY>
To create an integration use POST connect/integrations with Basic Auth included in request headers and following body:
{ "name": "Mobile Auth Demo", "provider": "google", "settings": { "client_id": "{provider_client_id}", "client_secret": "{provider_client_secret}" }, "redirect_uris": [ "application-url-scheme-placeholder://auth-callback" ], "scope": [ "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.readonly", "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email" ]}There are three required parameters in request’s body: name, provider, settings and recommended redirect_uri:
provideris an enum and might have in three following values:google,microsoft,imap.settingsis an object that need to includeprovider_client_idandprovider_client_secret.redirect_urishould include scheme that your mobile application can handle. Acceptable value for template app isnylas-demo-auth://but potentially could be anything your application could handle.- All other fields are optional.
Create and send your API request to create first integration. In case request has failed, visit Integrations API reference doc.
Step 2: Install ScribeJava Library
Section titled “Step 2: Install ScribeJava Library”Scribe Java library could be pulled directly from Maven Central repository.
Make sure your project is configured to work with Maven Central. Go to settings.gradle file and make sure mavenCentral() is in the repositories list:
repositories { google() mavenCentral()}To include Scribe library in your project, add the following dependency to your app’s build.gradle file:
implementation 'com.github.scribejava:scribejava-core:8.3.1'Alternatively, if your project is using Java and you have pom.xml file, add the following dependency there:
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.scribejava</groupId> <artifactId>scribejava-core</artifactId> <version>8.3.1</version></dependency>Sync gradle. Installation complete.
Step 3: Configure Secrets and Redirect URI
Section titled “Step 3: Configure Secrets and Redirect URI”OAuth process needs few account specific variables and environment where authorization will be performed. In order to configure that you need:
If you are using template app, go to Constants.kt and provide following parameters:
NYLAS_CLIENT_ID: Your Nylas application’s client ID.NYLAS_CLIENT_SECRET: Your Nylas application’s client secret.
In case you are integrating OAuth2.0 into your own application, consider some encrypted storage for sensitive data. We recommend to use DataStore for the newest API’s at least EncryptedSharedPreferences.
Example above made for presentation purposes only and we do not recommend to store any sensitive data, API keys, tokens as plain text in your project or under source control system. Please, consider encrypted approach to store sensitive data in a safe manner.
- Provide
BASE_URLinConstants.ktfile. - Provide exactly the same value used in creating integration in Step 1 for
CALLBACK_URI. - Provide
SCOPEinConstants.kt. Please, put scopes requested in Step 1 while creating integration.
Second part of OAuth configuration is setting up URI schemes to handle redirect URI’s once authorization is completed. Deep links are URIs of any scheme that take users directly to a specific part of your app. To learn more about integration using App Links, please visit Using App Links as Redirect URI on Android.
With your project (or template app) open in Android Studio, go to AndroidManifest.xml file. To create deep links, add intent filters to drive users to the right activity in your app, as shown in the following code snippet:
<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="" /></intent-filter>Provide exactly the same scheme used in Step 1 while creating integration.
You can specify <data android:host=""/> in case your redirect_uri contains some specific host that you need to handle.
Provide activity that will handle redirect with launch_mode:
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true" android:launchMode="singleInstance">Then open your activity to handle redirect inside. Override onNewIntent function in your activity.
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent)}Then add parsing of intent data and retrieve code query parameter value:
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent)
intent?.data?.getQueryParameter("code")?.let { //Push code further for processing here }}In case you are using template app you should look for a specific fragment and push code into it’s viewModel:
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent)
intent?.data?.getQueryParameter("code")?.let { val fragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.container) as MainFragment fragment.viewModel.performTokenExchange(it) }}Step 4: Integrate OAuth 2.0 Into Application
Section titled “Step 4: Integrate OAuth 2.0 Into Application”If you are using template app, look for MainViewModel.kt file and replace
fun performHostedAuth() { //Put code for hosted auth here}with following code:
fun performHostedAuth() { service = ServiceBuilder(Constants.NYLAS_CLIENT_ID) .apiSecret(Constants.NYLAS_CLIENT_SECRET) .callback(Constants.CALLBACK_URI) .responseType(Constants.RESPONSE_TYPE) .defaultScope(Constants.SCOPE) .build(NylasAPI())
val authURLBuilder = service.createAuthorizationUrlBuilder() .additionalParams(mapOf(Constants.Key.PROVIDER to Constants.PROVIDER))
authUrl.value = authURLBuilder.build()}The service instance should be retained since authorization is performed asynchronously. Template application has special variable defined within MainViewModel class.
Build and Run application to any Android device or simulator. Once build is finished you should see app like on the screenshot below:

Press Hosted Auth button. Application will start User Consent flow in external browser.
When the user clicks a deep link, a disambiguation dialog might appear. This dialog allows the user to select one of multiple apps, including your app, that can handle the given deep link.
Make sure you granted all the access requested on user consent screens. Once app is done you will see following application state:
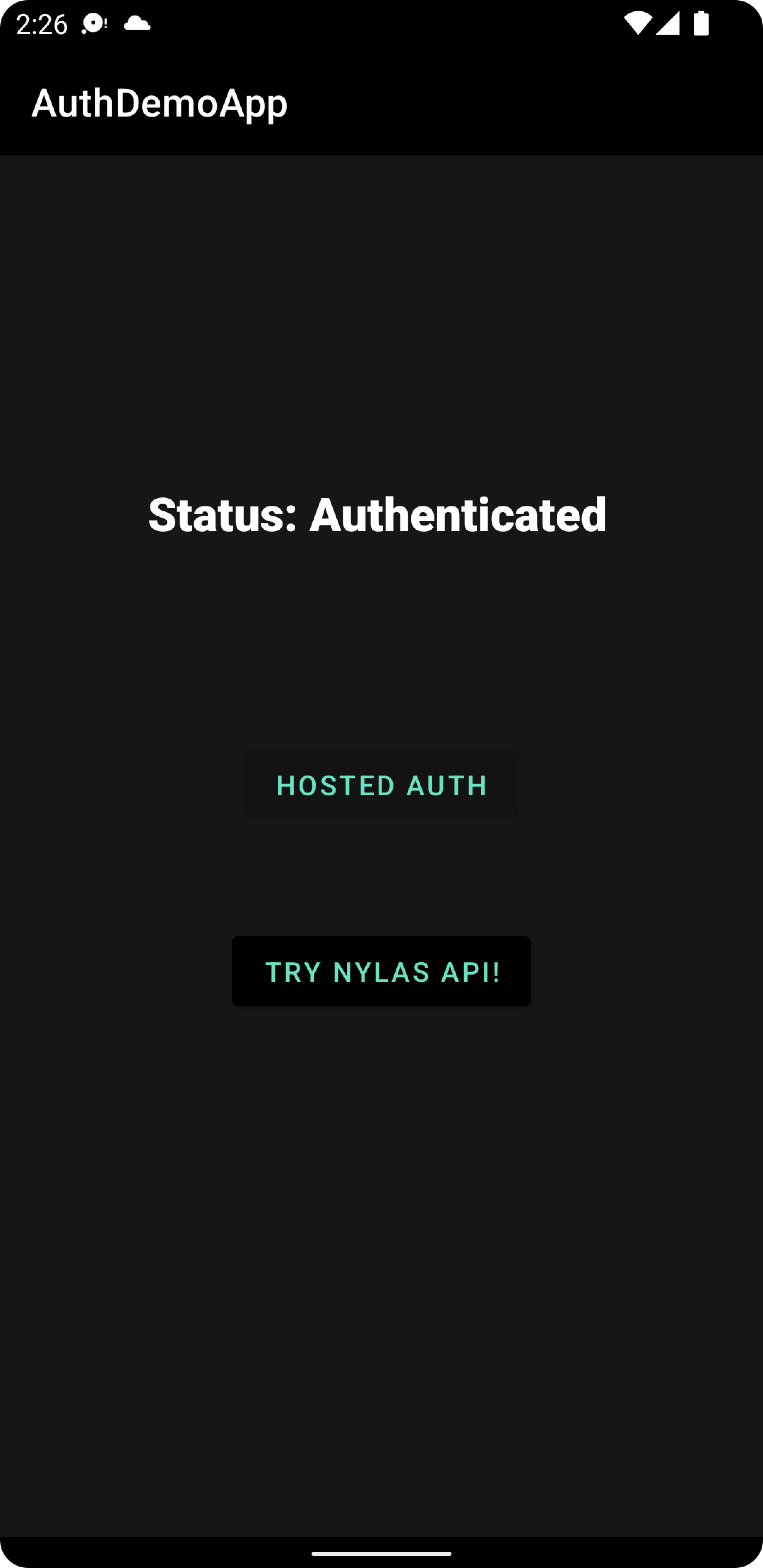
Template application running on Google Pixel 3a with authenticated session.
Step 5: Enabling PKCE Support
Section titled “Step 5: Enabling PKCE Support”Scribe supports proof key for code exchange aka PKCE. There are only few adjustments needed to enable PKCE support for OAuth 2.0:
Define codeVerifier and codeChallenge using following rules:
codeVerifiermight be any string up to 256 characters long.codeChallengeshould be SHA256 equivalent ofcodeVerifierand be base64 encoded (with removed padding).
Create instance of PKCE and set codeVerifier and codeChallenge parameters. Entire code sample listed below:
fun performHostedAuth() { service = ServiceBuilder(Constants.NYLAS_CLIENT_ID) .apiSecret(Constants.NYLAS_CLIENT_SECRET) .callback(Constants.CALLBACK_URI) .responseType(Constants.RESPONSE_TYPE) .defaultScope(Constants.SCOPE) .build(NylasAPI())
authBuilder = service.createAuthorizationUrlBuilder() .additionalParams(mapOf(Constants.Key.PROVIDER to Constants.PROVIDER))
val pkce = PKCE() pkce.codeVerifier = String().randomCodeVerifier()
pkce.codeChallenge = pkce.codeVerifier .sha256() .base64EncodedWithRemovedPadding()
authBuilder.pkce(pkce)
authUrl.value = authBuilder.build()}